
Summary
Ribosomal protein L2 is the largest protein component in the ribosome. It is located at or near the peptidyl transferase center and has been a prime candidate for the peptidyl transferase activity. It binds directly to 23S rRNA and plays a crucial role in its assembly. The three dimensional structure of the RNA-binding domain of L2 from Bacillus stearothermophilus has been determined at 2.3 Å resolution by X-ray crystallography using the Se-Met MAD method. The RNA-binding domain of L2 consists of two recurring motifs of about 70 residues each. The N-terminal half domain (pos. 60〜130) is homologous to the OB-fold and the C-terminal half (pos. 131〜201) is homologous to the SH3-like barrel. The residues Arg86 and Arg155, which have been identified by mutation experiments to be involved in the 23S rRNA binding, are located at the gate of the interface region between the two domains. The molecular architecture suggests how this important protein has evolved from the ancient nucleic acid binding proteins to create a 23S rRNA-binding domain in the very remote past.
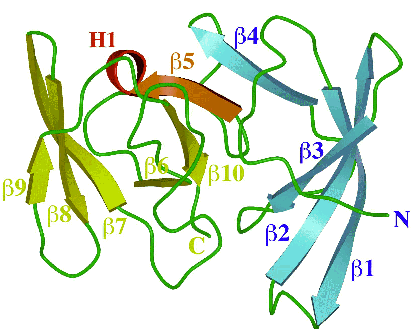
Figure Caption
RNA-binding domain of the ribosomal protein L2 from Bacillus stearothermophilus (BstL2-RBD). The molecule consists of two subdomains of approximately equal size. The N-terminal domain (colored blue) has an OB-fold homologous to the S1 domain and the C-terminal domain (colored yellow) has an SH3-like barrel motif. The fifth β-strand (colored red) and a 310 helix (H1) connect two subdomains.
References