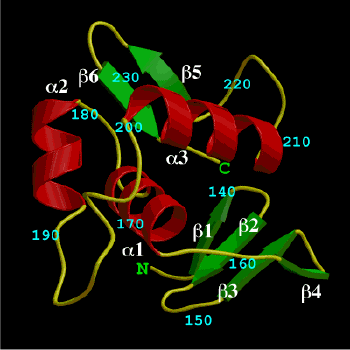

The structure of the C-terminal DNA-binding
domain of OmpR was determined by the X-ray crystallography at
2.0A resolution. OmpR is a positive regulator involved in
osmoregulation expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia
coli. The C-terminal half domain of OmpR, consisting of about
120 residues, exhibits an inherent DNA-binding ability specific
to the cognate promoters. The molecule consists of a
four-stranded beta-sheet and a three-helix bundle with a
C-terminal beta-hairpin. Well-conserved hydrophobic residues
cluster between the N-terminal four-stranded beta-sheet and the
C-terminal three-helix bundle, thus demonstrating the importance
of the four-stranded beta-sheet for the integrity of the
DNA-binding domain. Two helices, alpha2 and alpha3, and loop
between them create a structure somewhat similar to the
helix-turn-helix motif. The 'turn' region, consisting of 11
residues, forms an RNA polymerase contact site.
References