
Summary
The structure of human MRP8 in the calcium-bound form was determined at 1.9 Å resolution by X-ray crystallography. The structure was initially solved by MAD phasing of ytterbium (Yb)-substituted crystal and was refined against data obtained from Ca2+-bound crystal. The dimeric form of MRP8 was stabilized by the hydrophobic interactions between mutually wrapped helices. There were two EF-hand motifs per monomer, and each EF-hand bound one Ca2+ with a different affinity (;the affinity of C-terminal EF-hand (EF-2) to Ca2+ was stronger than that of the N-terminal EF-hand (EF-1). Furthermore, the replacement with Yb3+ occurred in the C-terminal EF-hand only, suggesting a more flexible nature for the EF-2 than for EF-1. This, combined with previous observations that helix in EF-2 (helix III) undergoes large conformational change upon calcium binding, suggests that C-terminal EF-hand (EF-2) plays a role as a trigger for Ca2+-induced conformational change.
Figure Caption
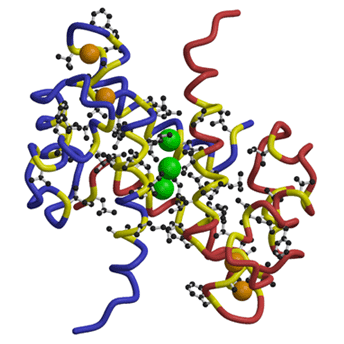
MRP8 dimer showing trapped xenon atoms in a hydrophobic cavity created at the monomer interface. Xenon atoms are shown as green spheres. The main-chains of two independent monomers are shown in different colors (blue and red) with their hydrophobic parts in yellow. Hydrophobic side-chains are also drawn. Calcium atoms are drawn in orange.
References