
Summary
Human MRP14 (hMRP14) is a Ca2+-binding protein from the S100 family of proteins.
This protein is co-expressed with human MRP8 (hMRP8), a homologue protein in myeloid cells,
and plays an indispensable role in Ca2+-dependent functions during inflammation.
This role includes the activation of Mac-1, the β2 integrin which is involved in
neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells.
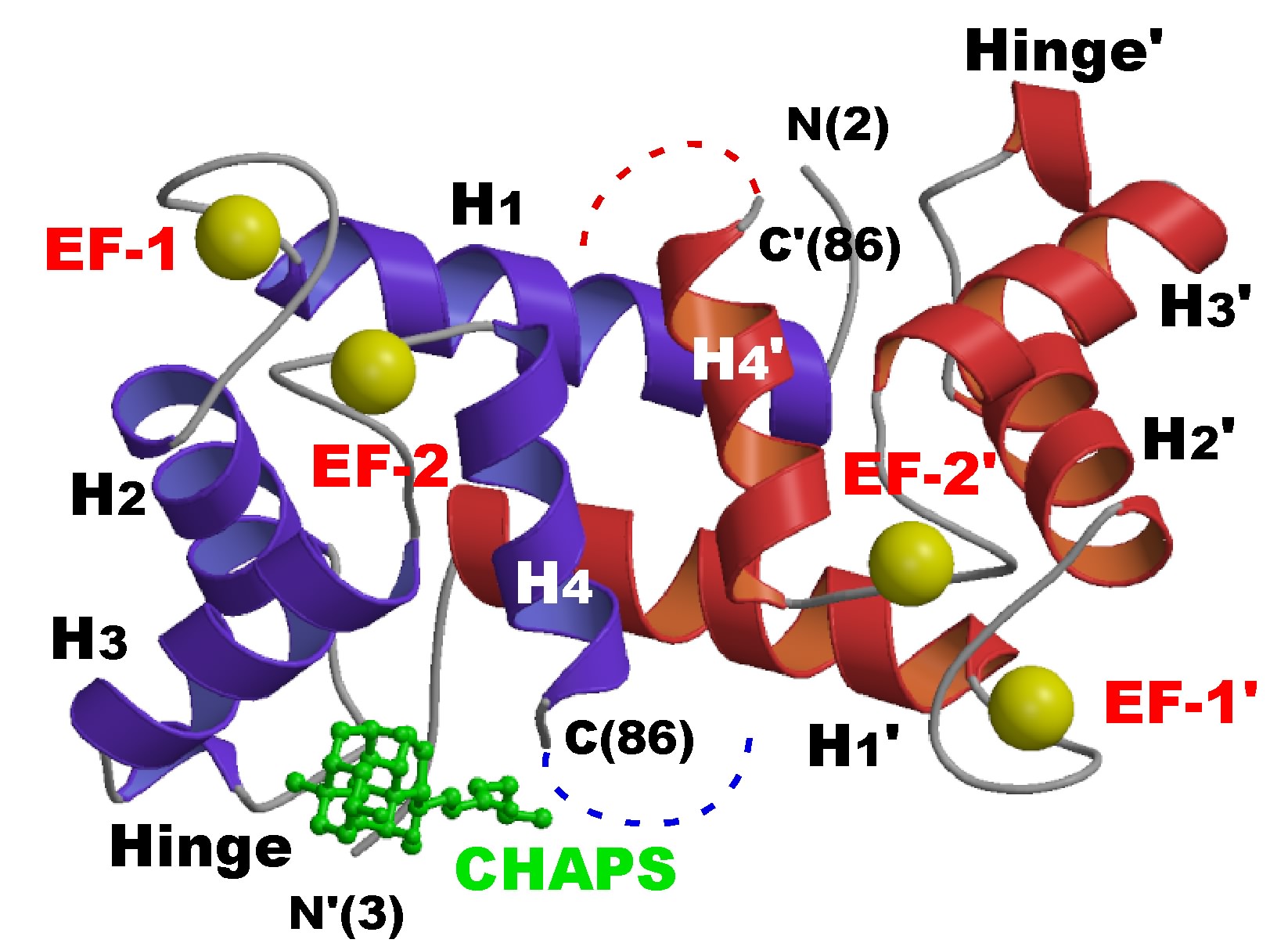
The crystal structure of the holo form of hMRP14 was analyzed at 2.1 Å resolution.
hMRP14 is distinguished from other S100 member proteins by its long C-terminal region,
and its structure shows that the region is extensively flexible.
In this crystal structure of hMRP14, CHAPS molecules bind to the hinge region that
connects two EF-hand motifs, which suggests that this region is a target-binding site of
this protein. Based on a structural comparison of hMRP14 with hMRP8 and human S100A12 (hS100A12)
that is another homologue protein, the character of MRP8/14 hetero-complex
and the functional significance of the flexibility of the C-terminal region of hMRP14 are revealed.
Figure Caption
The ribbon representation of human MRP14 dimer. Dotted lines show the direction of flexible C-terminal loop region. Yellow balls indicating calcium-ions. The bound CHAPS molecule is drawn in green ball and stick model.
References